When consumers decide to purchase any fashionable items or necessary goods, first they consider its quality then consider its price. So, to attract more satisfied customers, traders naturally try to keep only quality products in their outlets. According to the trade agreement, if the supplier provides defectiveitems during goods delivery buyer can penalize them.
 Quality problem is a major panic for manufacturers. Factory has to pay a lot of money, and it might affect on companies goodwill as well. That’s way the garments producers always pay much attention from the beginning to end stage to ensure good quality clothes. Sometimes buyer randomly inspects shipping goods after recipient by their assign Q.A at the warehouse but in maximum cases buyer inspects shipping goods at factory premises before delivering the finished garments to the destination by their assign Q.A. No matter which defects are being found in the final check up, it is an outcome of the immediately previous process.
Quality problem is a major panic for manufacturers. Factory has to pay a lot of money, and it might affect on companies goodwill as well. That’s way the garments producers always pay much attention from the beginning to end stage to ensure good quality clothes. Sometimes buyer randomly inspects shipping goods after recipient by their assign Q.A at the warehouse but in maximum cases buyer inspects shipping goods at factory premises before delivering the finished garments to the destination by their assign Q.A. No matter which defects are being found in the final check up, it is an outcome of the immediately previous process.So it would be better to repair or replace defective pieces at every process where it took place instead of the final stage.
Check Points
It is mention-able that defective garments increase inefficiency and company lost its goodwill. How defects come into finished garments? As we know, a lot of machines and many people are engaged for garments manufacturing process. Garments manufacturing is a chain process, and there is a definite possibility of producing some defective items in any consignment due to defective machine, imperfect process or human negligence. Sometimes repair task is costly and time-consuming but initially it is easy to repair or change the defective parts than found it in the final stage. If any faulty item passed through primary stage without identifying and rectification, it will make a big problem in the last stage and repaired or replacement cost will be much more than identifying it in the in the initial stage.
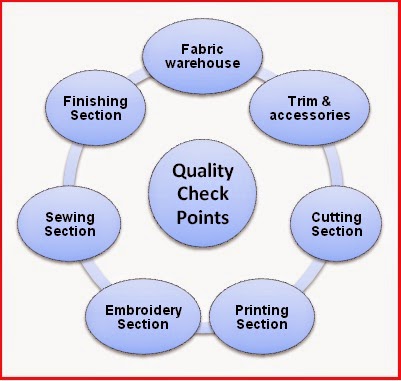
Production process always starts once received all necessary items to produce garments like fabrics, accessories, etc. in warehouse and finish after delivering of packed goods. Usually, manufacturers set quality checkpoints at the end of each stage to secure that only good quality items pass to the next level. To ensure product quality department wise checkpoints has been described by the following chart.
|
Fabric warehouse
|
Random inspection according to AQL 2.5. If random check becomes fail then require 100% inspection
|
|
Trim & accessories
|
Random inspection according to AQL 2.5. If random check becomes fail then require 100% inspection
|
|
Cutting Section
|
Marker checking > Fabric nature and test report check> Test cutting for QA Approval.
Fabric spreading > Relaxation if require > Cutting.
Sorting (Sticker, Numbering) > bundling. Check or audit cut panels.
|
|
Printing and Embroidery Section
|
100 % check up of printing panels
100% check up of embroidery panels
|
|
Sewing Section
|
Inline checkpoint (at vital operation)
Random checking (Roaming checking)
End of Line checking (apparently 100%)
Scrutiny of checked pieces
|
|
Finishing Section
|
Initial finishing inspection (after wash)
Final finishing inspection (After Pressing)
Internal shipment inspection
|
Fabric warehouse: Fabric store department should have facilities to inspect fabric item once received from the supplier that can issue to cutting department for next steps. 4 point system is one of most favorite fabric inspection method in garments industry to evaluate the quality level of the incoming fabric. According to this method, 10-20% of fabrics are being checked for renowned fabric provider. But 100% fabric has to be inspected for printed or power loom fabric. Usually, fabrics are examined by fabric checking machine or flat table with a light box.
1. Trims & Accessories: Trims or accessories are also very essential to make decent quality garments. Usually, trims are randomly inspected according to AQL 2.5. If random inspection becomes fail, then need 100% inspection.
2. Cutting section: As we know cutting section performs a great role in any apparel industry. Fabric cutting process is the most important part in cutting room because once the fabric has been cut, you may get very few option to rectify if serious mistakes happen. So cutting QC has to check major steps like
A) Marker checking > Fabric nature and test report check> Test cutting for Q.A Approval.
B) Fabric spreading > Relaxation if require > Cutting.
C) Sorting (Sticker, Numbering) > bundling.
C) Sorting (Sticker, Numbering) > bundling.
D) Check or audit cut panels.
3. Print checking: All garments may not have print functions. Cutting section should separate print panels once cut and check those cut panels then send to printing section for printing. Once printing is done at printing section, each panel is being checked properly. Defects what are found there that is print placement, misprint, color matching or print overlapping or shade variation has to replace for reprint.
4. Embroidery checking: Like printing all garments may not have embroidery functions. But if any garments having embroidery function then cutting section should separate embroidery panels once cut and check those cut panels then send to embroidery section to accomplish embroidery. After embroidery, those garment panels should inspect before issuing to sewing.
5. Sewing section: Following checkpoints have to maintain in sewing process to get good garments.
a) Inline inspection: Generally to produce the best quality garments, inline inspection set up in assembly line at vital operation.
b) Random inspection: In this process Q.A guy has to move around the line and randomly check pieces for each operation.
c) Traffic light inspection system: By this process each operator has given a card to measure their quality level. QC randomly goes to those operators and checks few pieces and gives them rating according to their performance.
d) End of Line inspection: A QC has to check complete garments at the end of the line. Defect free pieces are forwarded to the finishing department.
e) Audit of the checked pieces: Some garments exists this quality checking process. It is good practice to assure that only quality full garments are passed to packing section. All reject pieces have to repair before sending to packing department.
6. Finishing section: Finishing department checking process.
a) Internal finishing inspection: Before pressing the garment at finishing room should check it properly, it is known as initial finishing.
b) Final finishing inspection: The garments what already pressed are again checked then forward for tagging and packing.
c) Internal final audit: QC team do audit partially of packed garments. It has to be done to assure that before handing over the goods to buyer assign Q.A.
If above Quality Check Points strictly followed in Garment assembly process and reject pieces are repaired before sending to next steps, there is very little chance to have a reject garments at final inspection stage at the end of the production. These checkpoints may remove hassle in production line and will increase goodwill, efficiency, productivity as well as profit margin in any apparel industry.
You may like: Techniques to Improve Garment Quality




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.