Once upon a time, people wore hand-stitched clothes but due to the change of era and industrial revolution, various types of machines are being used in the garment industry while preparing clothes. Sewing machines are one of them which play a vital role in apparel making. Nowadays most of the apparel industry use eclectic sewing machine. It would be better if you had a basic idea about different parts of the sewing machine so that you can take care and troubleshoot easily when problems do arise. It is mandatory for the sewing operators to know the basic parts of sewing machine and how they work. In this article, I am going to elaborate on the sewing machine’s several parts and their functions with clear images for your easy understanding.
Parts of a Sewing Machine and Their Functions:
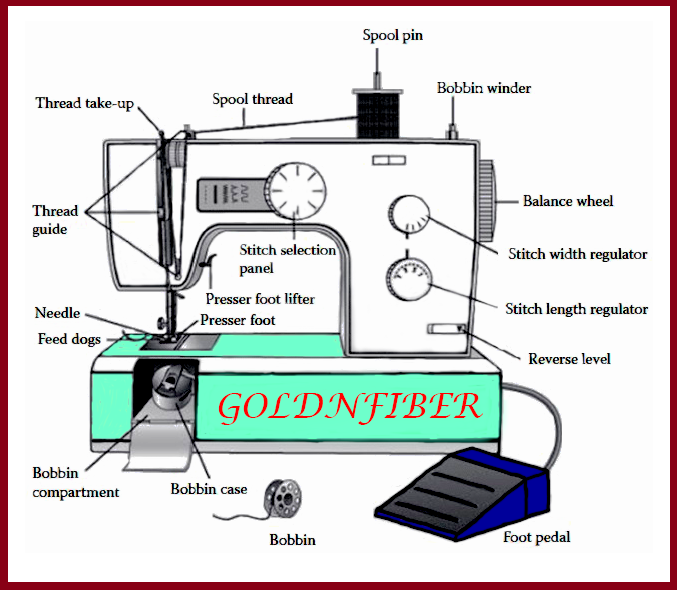
Please look at the following picture to know a electric sewing machine parts at a glance. The basic sewing machine components are shown in that picture and their functions with pictures are described below.
Functions of different parts of electric sewing machine with images:
An electric sewing machine exist several parts according to function. Almost 21 parts of a sewing machine are significant in its usage. Here we are giving a sewing machine parts list and sewing machine parts picture for your easy understanding. Sewing machine parts name and their functions are described below for your reference.
- Foot pedal:
It is a very simple tool who controls the speed of the machine which depends on the pressure applied on it. Sewing machine speed can be controlled by leg pressure. However, since the sewing machine speed may be adjusted with just one adjustment and is then started and stopped by pressing a button, it is not a necessary component of high-speed sewing machines.

- Power cord and switch:
The power cord, which must be tightly linked to the machine for a continuous flow of power, is what provides the machine with electricity. The power switch is used to electrically turn on and off sewing machines.

- Bobbin case:
In this situation, the bobbin needs to be mended. This is located behind the needle plate and typically has a piece of plastic that folds up to cover the bobbin case when stitching is not being done. In many sewing machines, bobbin casings cannot be swapped.

- Bobbin:
A bobbin is a little container that attaches to the bobbin casing and holds the bottom sewing thread. The bobbin winder fills the bobbins, and the thread should be spread equally throughout.

- Hand wheel:
To provide better control while positioning fabric beneath the needle, it is used to slowly raise and drop the sewing needle manually. The clutch knob, which is located inside the wheel, serves as a safety element by preventing the needle from jabbing up and down while winding a bobbin when the knob is pulled out.

- Reverse lever:
It is located on the machine’s front side. This is done to create reverse stitching while securing each seam with a stitch at the end.
- Bobbin winder:
This device is used to wind bobbin thread onto a bobbin that is empty. Bobbin winders can be found on the machine’s right or upper side.

- Pattern selector:
This tool is used to choose the type of stitch to be used while sewing on cloth, such as zigzag or embroidery stitches. In addition to straight stitches, a range of stitches can be chosen depending on the machine type.

- Throat plate:
It has stitching guide lines, two slots for the feed dog to travel through, and a hole for the needle to go through to the bobbin casing. It is a removable component that protects the sewing machine’s bobbin and base.

- Sewing light:
It makes it easier to thread the needle and lets you see your sewing both during the day and at night.

- Spool pin and holder:
It holds the thread while also directing the flow of the thread through the machine.

- Stitch length adjustment:
- The stitch’s length is determined by the stitch.
- The machine has a range of 0 to 4. The shortest stitch is zero, while the longest is four.
- The stitch length adjustment allows you to change how long the sewing machine’s stitches are. The feed dog, not the machine needle, is where the correction is made.
- The amount of cloth fed beneath the presser foot before the needle descends is inversely proportional to the stitch length.

- Needle and needle clamp:
A little screw secures the needle in the needle bar, which it fits into. The needle is secured in place with a needle clamp.

- Take-up lever:
The take-up lever pulls back the needle thread after each sewing to set the stitch and moves up and down during the stitch formation to supply the additional thread while making the loop. It is employed to maintain the ideal needle thread tension.

- Tension disks:
The stitch’s stiffness or looseness is determined by the thread tension. To ensure a uniform feed of the thread to the machine needle, tension disks regulate the pressure applied to the thread. The primary purposes of a tension device are to
- Maintain the smoothness in stitching
- Control the thread passage precisely
- Regulate the flow of the thread
- Position the thread to needle
Direct and indirect tension devices are two different types of tension devices. Parts like (a) pressure disk, (b) tension spring, (c) tension mounting bar, (d) thumb nut, and (e) pressure releasing unit are present in both types.
The tension dial with graduated numbers on it is used to adjust tension on high-speed, contemporary machines. The tension increases with the number and vice versa. The stitch line will be straight and even on both sides of the fabric when the tension is properly adjusted.

- Presser foot:
It holds the fabric in place from the top counter to the feed dog so that it may be fed through the machine. The material is pressed downward as it is passed through the needle.

17) Presser dial:
The presser dial determines the quantity of pressure to be exerted on the fabric through the presser foot. Lighter weight fabrics necessitate higher pressure for better control of fabric during stitching and vice versa.

18) Presser foot lever:
The presser foot is softly engaged and disengaged on the cloth against the feed dogs using this lever. The tension disks are disengaged when it is in the upward position and vice versa.

19) Thread cutter:
Sewing machine thread cutters are typically positioned behind the needle of the machine, making it easier to use the thread cutter while moving the cloth to the machine’s rear.

20) Slide plate:
The bobbin case is shielded from dust and grime by this plastic cover. Additionally, it provides access to the bobbin zone underneath the sewing machine so that other maintenance tasks can be completed there, such as changing the bobbins.

21) Feed dog:
Feed dogs are a mechanical component resembling teeth that, in conjunction with the presser foot, facilitate the movement of cloth by one stitch. Furthermore, it governs the stitch length by the manipulation of the fabric’s displacement per individual stitch.

You may like: How the sewing machine came?